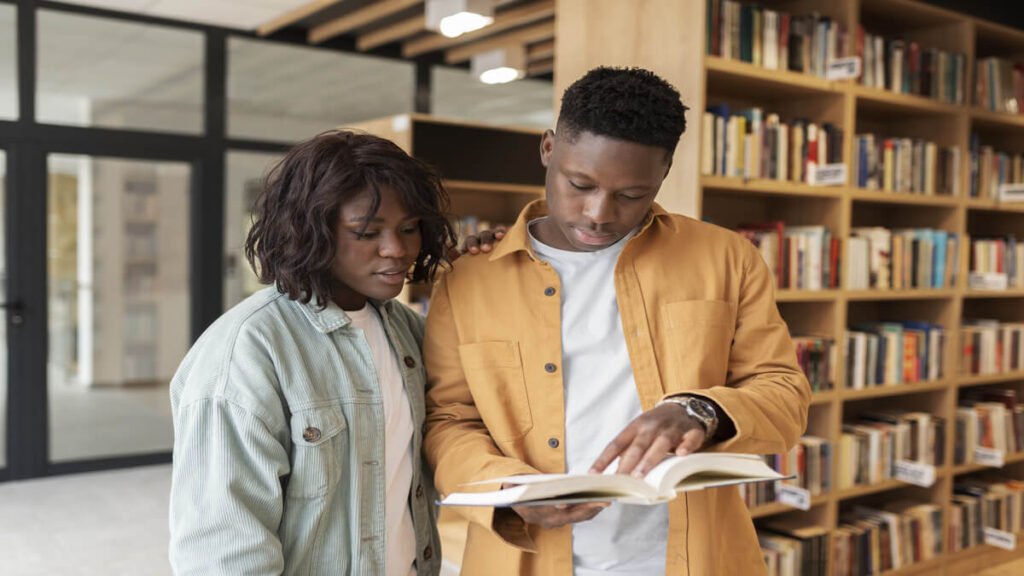
As thousands of South African students rely on the National Student Financial Aid Scheme (NSFAS) for their educational aspirations, understanding the list of courses funded by NSFAS is crucial in making informed decisions about your studies.
NSFAS, serving as a lifeline for many, ensures that financial constraints do not hinder the dreams of students pursuing higher education. By specifically targeting a wide range of courses at public universities and TVET colleges, NSFAS not only facilitates access to tertiary education but also aims to align its funding with the country’s pressing skill demands.
This expanded focus helps students to choose career paths that are not only fulfilling but also in line with the economic and developmental goals of South Africa. As we delve deeper into the specifics of NSFAS-funded courses, prospective students are empowered with the knowledge to navigate their educational journey more effectively, optimizing the support NSFAS offers to transform their future and by extension, the future of the nation.
Introduction to NSFAS Funding
NSFAS aims to remove financial barriers for students from low-income households, enabling them to achieve their educational aspirations. By covering tuition fees, accommodation, and study materials, NSFAS ensures that eligible students can focus on their studies without the burden of financial constraints.
Key Courses Funded by NSFAS
NSFAS funds an array of courses within the public tertiary education system, focusing on programs that align with the nation’s skills shortages and employment demands. Here are some of the major fields and courses supported by NSFAS:
1. Engineering and Built Environment
- Civil, Mechanical, and Electrical Engineering
- Urban and Regional Planning
- Quantity Surveying and Construction Management
- Chemical Engineering: Focused on the design, operation, and management of processes that transform raw materials into valuable products.
- Mining Engineering: Prepares students for careers in mining and mineral processing, emphasizing sustainable and safe extraction methods.
- Architectural Studies: Combining art and science to design buildings and structures, focusing on aesthetics, functionality, and environmental sustainability.
- Geomatics: Involving the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data relating to the Earth’s surface, essential for planning, construction, and environmental management.
- Environmental Engineering: Addressing environmental challenges through the application of engineering principles, aiming to improve waste management, water and air quality, and public health.
- Water Care: Focused on water conservation, treatment, and management, preparing students for roles in ensuring safe and efficient water use and quality.
- Electronics and Computer Engineering: Covering the development and application of electronics and computer technologies in various industries, including telecommunications, manufacturing, and robotics.
2. Health Sciences
- Nursing
- Pharmacy
- Clinical and Health Sciences, including Medical Practitioners
- Dental Sciences: This includes degrees in Dentistry and Dental Therapy, focusing on oral health, treatment, and preventive care.
- Public Health: Offering insights into healthcare policy, epidemiology, and health education, aiming to improve health outcomes on a community and national level.
- Physiotherapy: Training students in the management and treatment of physical disorders and injuries through physical methods such as exercise and massage.
- Occupational Therapy: Focused on enabling people to participate in everyday activities through therapeutic techniques, addressing physical, psychological, and social barriers.
- Radiography: Involving the use of radiographic technology for diagnostic purposes, such as X-rays and MRI scans, playing a critical role in medical diagnostics.
- Biomedical Sciences: Providing a foundation in understanding the biological principles underlying health and disease, leading to roles in research, diagnostics, and therapeutic sciences.
- Optometry: Training individuals in the examination, diagnosis, treatment, and management of disorders and diseases of the visual system.
- Dietetics and Nutrition: Focused on the role of food and nutrition in health, disease prevention, and management, critical for promoting healthy lifestyles and managing chronic diseases.
3. Education
- Bachelor of Education (BEd) degrees for various phases and subjects
- Postgraduate Certificate in Education (PGCE) for graduates seeking to enter the teaching profession
- Early Childhood Development (ECD): Specializations in education for children from birth to grade R, focusing on foundational learning and development.
- Adult Education: Degrees aimed at training educators to teach adult learners, emphasizing literacy, vocational training, and continuing education.
- Special Needs Education: Preparing educators to support learners with diverse educational needs, including disabilities and learning difficulties.
- Educational Leadership and Management: For those aspiring to take on administrative and leadership roles within educational institutions and systems.
- Educational Psychology: Combining the principles of education and psychology to support learners’ emotional, social, and educational development.
- Curriculum Development: Focused on the design and implementation of educational programs and assessments, aiming to improve teaching and learning outcomes.
4. Information Technology and Computer Science
- Bachelor of Science (BSc) in Computer Science: This foundational course covers algorithms, data structures, software design, and the principles of computer hardware.
- National Diploma in Information Technology: Offers practical skills and knowledge in IT support, network administration, and web development.
- Bachelor of Information Technology (BIT): A comprehensive degree covering a broad range of IT topics, including information systems, network security, and database management.
- Software Engineering: Focused on the development, design, and maintenance of software systems, preparing students for careers in software development and engineering.
- Cyber Security: Specializing in the protection of information systems against theft, damage, and unauthorized access, this field is increasingly important in safeguarding digital infrastructure.
- Data Science and Analytics: Teaching students how to analyze and interpret complex data to make informed decisions, a skill highly valued across multiple industries.
- Digital Design and Media: Combining creative design with digital technology, this qualification prepares students for careers in digital marketing, graphic design, and multimedia production.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Focused on creating systems that can learn and make decisions, preparing students for cutting-edge careers in AI development and research.
- Network and Systems Administration: Offering in-depth knowledge on the management and maintenance of computer networks, essential for the smooth operation of IT infrastructures.
- Cloud Computing: Teaching the design, deployment, and management of cloud services, reflecting the shift towards cloud-based technology solutions in business and industry.
5. Business and Management Studies
- Bachelor of Commerce (BCom) in Accounting, Economics, and Management: Offers a foundational understanding of business principles, financial accounting, economics, and management strategies.
- National Diploma in Business Management: Provides practical skills and knowledge in business operations, management, and entrepreneurship.
- Bachelor of Commerce (BCom) in Finance: Focuses on financial markets, corporate finance, investment management, and financial planning, preparing students for careers in the finance sector.
- Bachelor of Commerce (BCom) in Marketing Management: Covers the strategies and techniques of marketing, including digital marketing, consumer behavior, and brand management.
- Bachelor of Commerce (BCom) in Human Resource Management: Prepares students for careers in HR, focusing on recruitment, labor relations, performance management, and organizational development.
- Bachelor of Commerce (BCom) in Supply Chain Management: Teaches the intricacies of logistics, procurement, distribution, and operations management, essential for efficient business operations.
- Bachelor of Business Administration (BBA): Offers a broad perspective on business management, including leadership, organizational behavior, and strategic management.
- Bachelor of Commerce (BCom) in Entrepreneurship: Equips students with the skills to start, manage, and grow their own businesses, focusing on innovation, venture creation, and entrepreneurship dynamics.
- Bachelor of Commerce (BCom) in International Business: Focuses on global business strategies, international trade, and cross-cultural management, preparing students for a career in international commerce.
- Bachelor of Commerce (BCom) in Information Systems: Bridges the gap between business and IT, teaching students how to leverage technology to solve business problems and improve processes.
6. Agriculture and Environmental Sciences
- Bachelor of Science (BSc) in Agriculture: Covering agricultural production, management, and sustainable farming practices.
- Diploma in Forestry and Fisheries: Specialized training in the management and conservation of forest and aquatic resources.
- Environmental Science: Focusing on the study of natural processes, how they are affected by human activities, and strategies for conservation.
- Wildlife Management: Dedicated to the conservation and management of wildlife species and their habitats.
- Horticulture: Concentrating on the cultivation of plants for food, comfort, and beautification, including fruits, vegetables, flowers, and ornamental plants.
- Agronomy: The science of soil management and crop production, essential for ensuring food security and sustainable agricultural practices.
- Viticulture and Oenology: Specializing in the study of grape cultivation and wine production, important for South Africa’s wine industry.
- Aquaculture: Focused on the breeding, rearing, and harvesting of fish, shellfish, and aquatic plants in controlled environments.
- Environmental Engineering: Applying engineering principles to solve environmental problems, including water and air pollution control, waste management, and renewable energy.
7. Law
- Bachelor of Laws (LLB): Provides a comprehensive understanding of the legal system, preparing students for careers in law, advocacy, and legal consultancy.
- Bachelor of Arts (BA) in Criminology and Law: Combines the study of criminal justice systems with legal principles, focusing on crime prevention, legal ethics, and penal policy.
- Diploma in Paralegal Studies: Prepares students for supportive roles in legal services, focusing on legal research, document preparation, and case management.
- Bachelor of Commerce (BCom) in Law: Offers a blend of commercial and legal studies, ideal for careers in corporate law, commercial regulation, and legal aspects of business management.
Related: A Comprehensive Guide to the 10 NQF Levels and Qualifications in South Africa
Exclusions: Courses Not Funded by NSFAS
While NSFAS provides broad coverage, certain courses fall outside its funding scope. These include but not limited to:
- Postgraduate programs (beyond a PGCE): NSFAS focuses its resources on undergraduate degrees and diplomas to support students entering higher education for the first time. This includes a Bachelor’s degree, national diploma, higher certificate, and the Postgraduate Certificate in Education (PGCE) for those transitioning into teaching. Advanced studies such as Honours, Masters, and Doctoral degrees are beyond its funding mandate.
- Courses offered by private institutions: NSFAS funding is designated for public universities and TVET colleges. This aligns with the scheme’s objective to support education that is accessible to all, utilizing public funds to bolster the public education system. Courses at private colleges, universities, or training centers are excluded from NSFAS funding.
- Non-credit bearing courses, short courses, and part-time studies: The focus of NSFAS is on full qualifications that lead to an official academic credential. Non-credit bearing courses, including skills development workshops and certificate programs that do not accumulate credits towards a formal qualification, are not covered. Similarly, short courses that are completed in a shorter duration than a typical academic term and part-time studies that do not fall into the full-time study category are excluded.
- Courses with high employment market saturation: NSFAS strategically funds courses that align with the national critical skills list and areas with high employment potential. Courses leading to fields where there is a surplus of professionals may not be prioritized for funding, ensuring that the investment in education translates to meaningful employment opportunities.
- Luxury and lifestyle courses: Courses considered to be more about personal enrichment rather than career-oriented or critical to the country’s development, such as certain arts, fashion design, and culinary arts programs, may fall outside of NSFAS’s funding criteria.
- Distance learning programs: While some distance learning programs offered by public institutions may be funded, generally, NSFAS prioritizes full-time, contact learning. This is because the comprehensive support package, including allowances for personal care and accommodation, is tailored towards students who are studying on campus.
Eligibility and Application Process
Eligibility for NSFAS funding is determined based on financial need and academic performance. South African citizens enrolled or planning to enroll in public universities or TVET colleges for undergraduate courses are encouraged to apply. The application process is straightforward, requiring prospective students to submit their applications via the NSFAS online portal, along with supporting documentation.
Read More: Understanding the New NSFAS Eligibility And Allowance Adjustments in 2024
Duration and Scope of NSFAS Funding
NSFAS covers the full duration of a student’s study program, provided the student maintains satisfactory academic performance.
What does NSFAS cover? NSFAS offers comprehensive funding that encompasses several critical aspects of a student’s educational expenses:
- Tuition Fees: NSFAS covers the full cost of tuition, ensuring that students can attend courses without the worry of unpaid fees.
- Accommodation: For students who do not live at home, NSFAS assists with the costs associated with university-approved housing, which can be either on-campus or off-campus, depending on the availability and the student’s preference.
- Books and Learning Materials: An allowance for textbooks and other essential learning materials is provided, which is crucial for completing coursework and preparing for exams.
- Living Expenses: To help manage day-to-day expenses, NSFAS provides a living allowance, which can be used for food, transport, and other necessary expenditures.
Annual Reapplication is Necessary It’s important to note that NSFAS funding is not automatically renewed each year. Students are required to reapply annually to prove their ongoing eligibility for the scheme. This process includes demonstrating satisfactory academic progress and meeting any other requirements set forth by NSFAS. Failure to reapply or meet the necessary criteria can result in the discontinuation of funding, which could severely impact a student’s ability to continue their education.
Ensuring Continued Eligibility To maintain their NSFAS funding, students must meet the academic requirements set by their respective institutions. This typically means passing all courses and progressing to the next academic year. NSFAS monitors students’ academic performance and other factors to ensure that the funds are being used to support eligible students who are committed to completing their studies.
The Courses Funded by NSFAS offer a ladder of opportunity for many South African students aiming to break the cycle of poverty through education. By providing financial support for a wide range of courses in critical fields, NSFAS plays an instrumental role in building the nation’s workforce and addressing the skills gap in various sectors. Students are encouraged to leverage this support, pursue their academic goals, and contribute to South Africa’s development.